Daily Archives: 12 January, 2019
It is true that it feels like I have had a huge exam. I still need some time to do nothing before I continue to write. I listen a lot to music, make good food, watch entertaining series. Read some. Write here. Meanwhile, I have thought of teaching. Pharmacology. Basic pharmacology. Classical receptor pharmacology. Since I work at a pharmacy, I work daily with teaching. I might not explain the exact pharmacological mechanism for the exerted clinical effect, but at least I explain how to use the medicin in the right way to get the best effect of the drug.
If you use a too low dose you don’t get any effect of the drug. And if you use a to high dosage, significant adverse effects may occur. This is called the therapeutic window. Furthermore, potency is an important term within pharmacology. Potency of a drug is defined as that concentration at which the drug elicits 50 percent of its Emax (E = effect, eg blood pressure). If a drug is potent it means that a very low dose is needed to have a significant clinical effect.
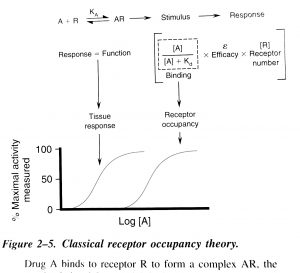
Something that is very important to keep in mind is that biologic variation is very common. That is variation in magnitude of a biological response (eg cognitive function) in a population of patients given the same dose of the drug. This variation depends on eg how the drug binds to the receptor and this is clarified in the illustration above (Goodman & Gilman). You see the drug concentration on the X-axis and the effect of the drug on the Y-axis. The affinity to the receptor is explained by the chemical forces that cause the drug to associate with the receptor, like a hand in a glove. There is always an equilibrium between the drug and the receptor. This can be measured by complex mathematical formulas like the illustration above.
The law of mass action.
Two other important terms within pharmacology are: agonist and antagonist. An agonist stimulates the receptor to exert a specific biological response, and an antagonist block the receptor. Metoprolol is a typical β1-antagonist where pulse and blood pressure are lowered due to blockade of the adrenergic receptors located mainly in the heart.
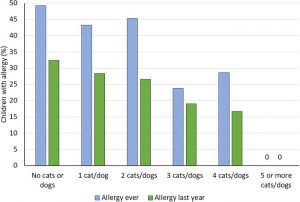
This is a brief theoretical introduction to basic pharmacology. To make it easier to understand, there is an illustration from Hesselmar and co-workers (2018), where they studied if animal allergen in early life can reduce the risk to develop allergy. It seems like dog- and cat exposure can protect against allergic manifestations like asthma. A “mini-pharm” effect that was dose-response dependent. The full study can be downloaded here:

 Svenska
Svenska